



Blog | Technology
23rd August, 2024

Vaishnavi Vaidyanathan is a highly skilled cybersecurity expert with over 18 years of experience in the field. She is recognized for her strategic thinking and hands-on approach and has a strong track record in designing and implementing robust security solutions to safeguard organizations from emerging threats and vulnerabilities. Vaishnavi specializes in developing cybersecurity strategies to protect critical infrastructure and sensitive organizational data. This includes implementing advanced threat detection systems, adopting cutting-edge encryption technologies, establishing a rigorous incident response framework, and implementing advanced identity management for clients.
Phani Kishore Burre is the Managing Director and Global Practice Head for Digital Infrastructure at Brillio. With 25 years of experience, he has successfully architected multiple platforms and accelerators, led cloud migrations, managed services for hybrid clouds, and many more for our customers with leading NPS scores. Phani partners with C-suite executives of Fortune 500 enterprises for digital transformation initiatives. He believes in enriching people by actively sharing his acumen on transformation themes and provides insights to help in research across industries and technologies.
At Brillio, sophistication in cyber threats has become a point of paramount focus for our clients to adopt artificial intelligence to safeguard their businesses.
Cyber threats are evolving alarmingly, with attackers employing more sophisticated methods to breach systems, steal sensitive information, and disrupt operations. Traditional cybersecurity measures, while still essential, are no longer sufficient to combat these advanced threats. AI offers powerful tools and strategies to enhance our defense mechanisms against these threats.
As the frequency of cyber attacks continues to rise, cyber security has become a top priority for companies. Despite the increased attention to this issue, cyber security risks are still growing. Every year, the number of cyber attacks on companies, governments, and individuals keeps rising. With more organizations transitioning to remote work, the migration of workloads from traditional networks is speeding up, resulting in an expanded potential cyber attack surface. Simultaneously, cyber attackers are becoming more sophisticated, adapting their methods as enterprises improve their ability to detect and respond to attacks.
Many cyber criminals now utilize advanced techniques that make their activities hard to detect, use automation to increase their success, and target businesses’ highest-value assets. As the potential payoff increases, cyber crime is estimated to cost trillions of dollars by 2025.
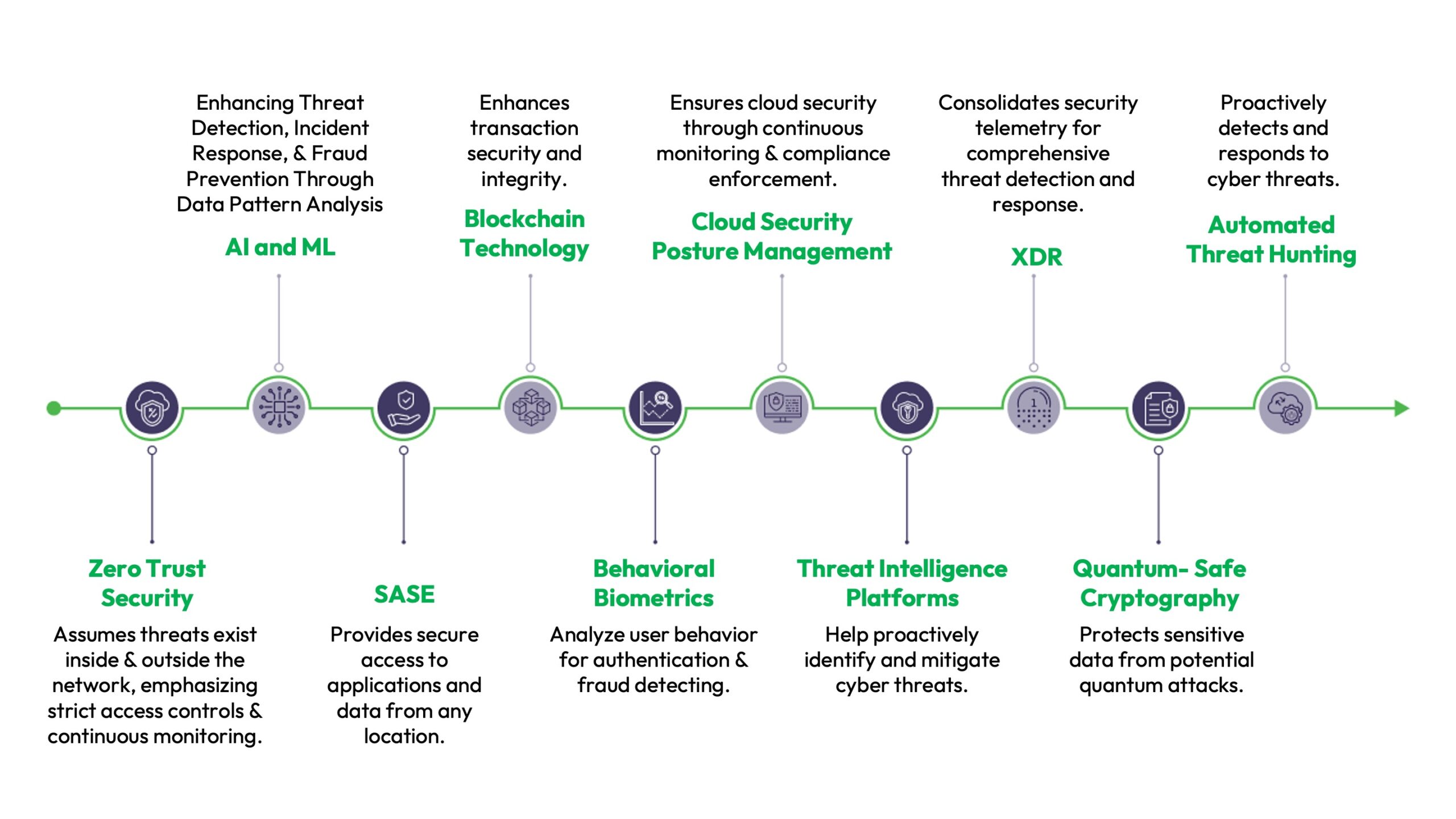
Let’s look at a few use cases of how AI can benefit cyber security.
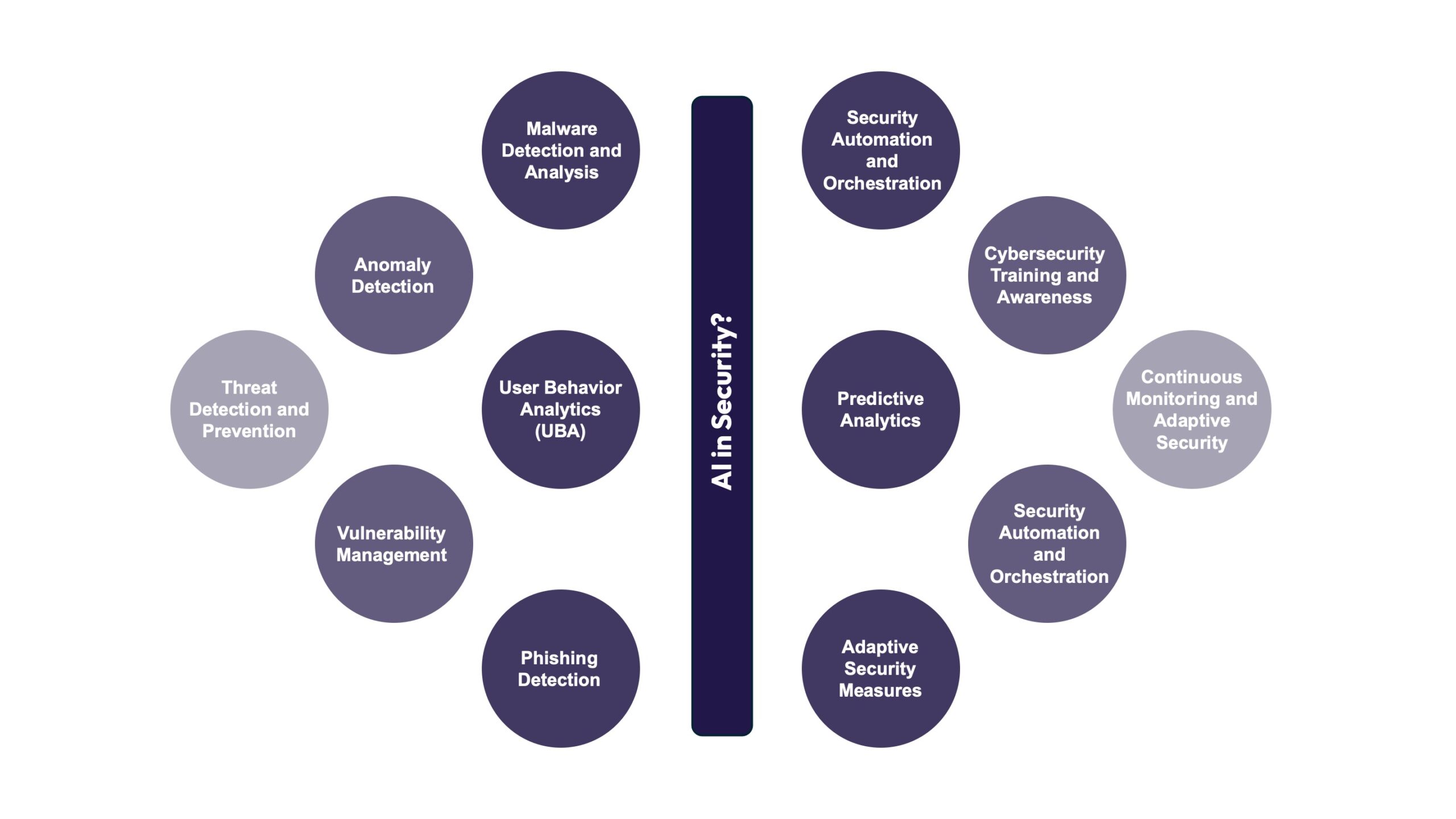
Threat detection and prevention: AI-powered intrusion detection and prevention systems proactively monitor network traffic for malicious activities, providing real-time threat blocking. AI-based malware detection solutions identify and neutralize malware infections across the IT infrastructure, including endpoints, servers, and network devices. AI-driven email security solutions detect and block phishing attacks, spam, and other email-based threats targeting employees, offering a proactive defense against potential threats.
Anomaly detection: AI-based anomaly detection systems identify unusual patterns or behaviors within the IT infrastructure that may indicate potential security incidents, such as unauthorized access attempts or insider threats. They can monitor system logs, user activity, and network traffic using AI-driven analytics tools to detect deviations from normal behavior and proactively mitigate security risks.
Vulnerability management: AI-powered vulnerability assessment tools prioritize security vulnerabilities in the IT infrastructure, including software vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weak authentication mechanisms. Employ AI-based risk-scoring algorithms to prioritize remediation efforts based on the severity of vulnerabilities and their potential impact on business operations.
Malware detection and analysis: AI algorithms can recognize patterns and characteristics of known malware strains, allowing them to identify and block malicious software before it can compromise systems or steal sensitive data. Additionally, AI-powered malware analysis tools can analyze the behavior of unknown malware samples to identify previously unseen threats.
User Behavior Analytics (UBA): AI-driven UBA solutions use AI algorithms to analyze and interpret user behavior data and monitor user activities to identify suspicious or unauthorized actions. UBA systems can detect insider threats, compromised accounts, and other security risks by analyzing login patterns, file access behavior, and application usage.
Phishing detection: AI-powered email security solutions utilize machine learning to analyze incoming emails for indications of phishing attacks, such as suspicious links, attachments, or impersonation attempts. These solutions automatically flag potentially malicious emails, helping to prevent users from becoming victims of phishing scams.
Security automation and orchestration: AI technologies help automate routine security tasks such as scanning vulnerabilities, patch management, and incident response. By streamlining these processes and reducing manual intervention, AI-driven security automation tools enable organizations to respond more quickly and effectively to security incidents.
Predictive analytics: AI algorithms can analyze historical security data to identify trends and predict future cyber threats. By leveraging predictive analytics, organizations can proactively implement security measures to mitigate all potential risks before they materialize.
Adaptive security measures: AI-powered security solutions can dynamically adjust security controls and policies based on evolving threat landscapes and changing organizational needs. This adaptive approach helps organizations avoid emerging threats and ensure that security measures remain effective.
Cybersecurity training and awareness: AI-driven training platforms use personalized learning algorithms to deliver targeted cybersecurity training and awareness programs to employees. By tailoring training content to individual learning styles and knowledge gaps, these platforms empower employees to understand cybersecurity best practices and recognize potential threats better, enhancing their cybersecurity awareness and confidence.
Security automation and orchestration: Integrate AI-driven security automation tools to automate repetitive security tasks, such as patch management, policy enforcement, and compliance checks, to improve operational efficiency and reduce manual workload. Implement AI-powered security orchestration platforms to coordinate and streamline security workflows across disparate security tools and technologies, enabling faster response to security incidents and threats.
Continuous monitoring and adaptive security: Establish AI-driven constant monitoring capabilities to provide real-time visibility into the IT infrastructure’s security posture and promptly detect emerging threats or vulnerabilities. Implement adaptive security measures that leverage AI-based analytics and machine learning to dynamically adjust security controls and policies based on changing threat landscapes, user behavior, and business requirements.
By integrating AI-driven tools and technologies into their IT infrastructure, organizations can strengthen their cyber security defenses, enhance threat detection and response capabilities, and better protect against evolving cyber threats. Additionally, ongoing monitoring, evaluation, and optimization of AI-based security solutions are essential to ensure effectiveness and adaptability in the face of emerging cyber risks.
However, it also comes with various risks and challenges that need careful consideration. AI systems rely on data to identify historical trends, but hackers can access the training data and manipulate it to introduce biases, undermining the models’ effectiveness. Hackers can alter data and use AI techniques to develop sophisticated malware that adapts to avoid detection by even the most advanced cybersecurity software.
AI model performance heavily depends on the quality and quantity of training data. If the system doesn’t receive enough high-quality training data or if the data contains biases, it can compromise the accuracy of the AI system. Inadequately trained models may also produce false positives, giving a false sense of security and exposing organizations to undetected threats and significant losses.
AI models, typically trained on real-world user data to understand user patterns, underscore the importance of robust data protection measures such as data masking or encryption. Without these, sensitive user data becomes vulnerable to privacy and security breaches, favoring malicious actors. Like any other software, AI systems are susceptible to cyber attacks. Hackers can input poisoned data into these models to manipulate their behavior for malicious purposes.